Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunohistochemistry
The expression of the special AT-rich sequence-binding protein SATB2 was analyzed in MCC n 20 together with other forms of skin cancer. Approximately 25 Danish patients are diagnosed each year.

Merkel Cell Carcinoma A Review And Update On Current Concepts Diagnostic Histopathology
Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is a rare aggressive skin cancer with neuroendocrine differentiation.
Merkel cell carcinoma immunohistochemistry. Although rare compared with other skin cancers the incidence of Merkel cell carcinoma in the USA tripled between 1986. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural analyses are usually helpful in differentiating these neoplasms. Distinction between primary cutaneous Merkel cell carcinoma and metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma in the skin is based on the immunohistochemical profile of the tumor and clinical pathologic correlation ie.
Merkel cell tumors stain positively for NSE as would any APUD cell. Risk factors include long-term ultraviolet UV exposure Merkel cell polyomavirus MCV infection immunosuppression and lymphoproliferative disorders such as chronic lymphocytic. These can lead to diagnostic difficulty.
Based on its origin the cancer cell type is called a neuroectodermal tumor. Other positive stains include CD56 chromogranin synaptophysin neurofilament. The pathological differential diagnosis includes basal cell carcinoma melanoma lymphoma and metastatic small cell lung carcinoma.
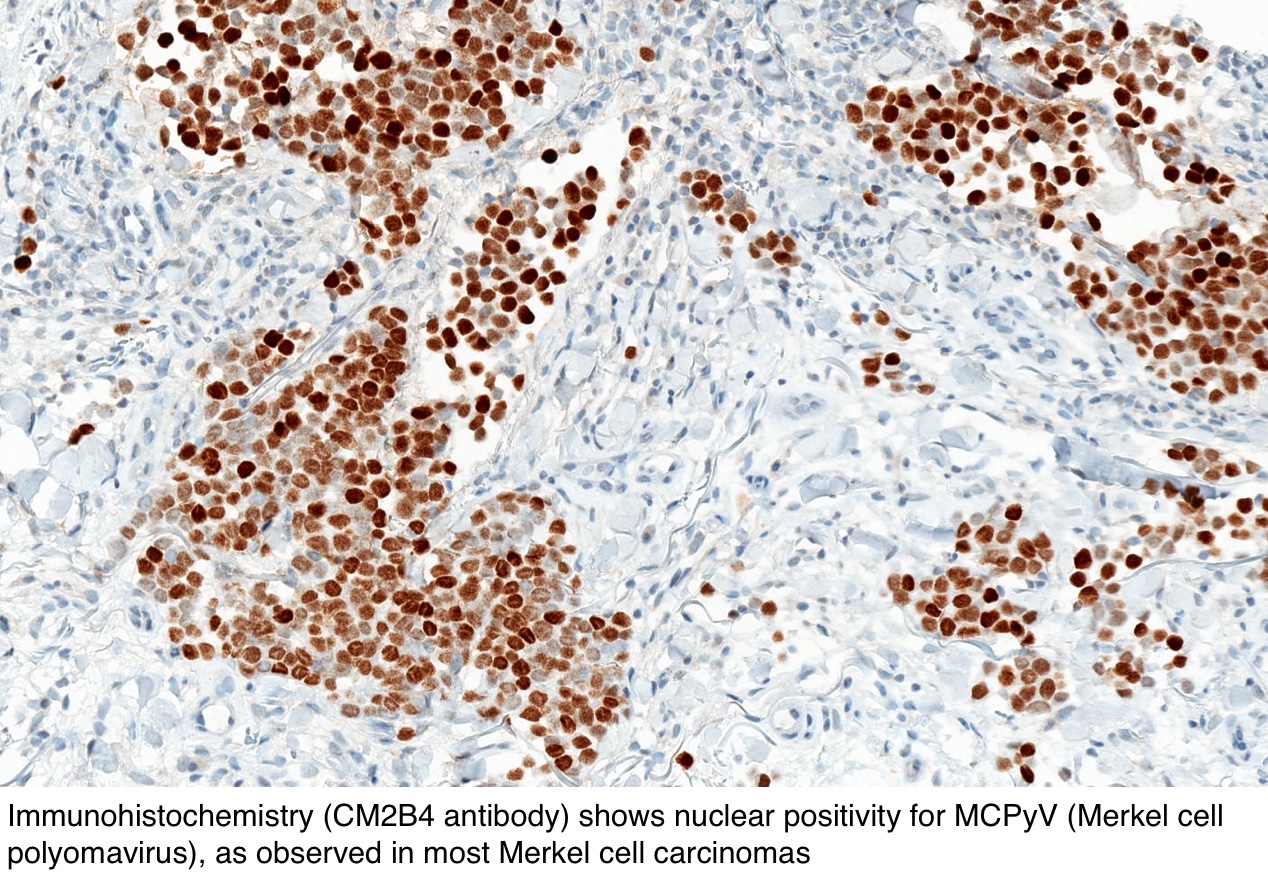
It is also found to be more common among patients with lymphoma and those receiving immunosuppressive therapy 13. Histopathologic diagnosis frequently requires support by immunohistochemistry. ALK and EGFR expression by immunohistochemistry are associated with Merkel cell polyomavirus status in Merkel cell carcinoma Histopathology.
Immunohistochemistry is often used to confirm Merkel cell carcinoma MCC. Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is a cutaneous neoplasm histopathologically difficult to differentiate from other small blue cell neoplasms. The risk for Merkel cell carcinoma is increased 13-fold among HIV patients 12 and 10-fold after solid organ transplantation.
The objectives of the current study were 1 to examine the immunohistochemical profile of. Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is a rare neuroendocrine carcinoma. Merkel cell carcinoma.
Diagnostic accuracy has improved through immunohistochemical markers such as CK-20. Special studies of Merkel cell carcinoma Immunohistochemical studies are essential. The literature records many examples of Merkel cell carcinoma MCC exhibiting aberrant immunohistochemical profiles.
The diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma is mainly based on the association of clinical data microscopic features of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma. The tumour typically shows characteristic perinuclear staining with CK20 figure 5. We assessed the usefulness of several immunohistochemical stains in distinguishing these two neoplasms including cytokeratin 7 cytokeratin 20 CK20 neuron-specific enolase chromogranin synaptophysin neurofilaments NF thyroid-transcription factor-1 TTF-1 CD56 antigen S-100 protein vimentin c-erbB-2 oncoprotein and CD117 antigen.
With immunohistochemistry the tumor cells stain for both neuroendocrine ie synaptophysin and chromogranin A and epithelial markers. The epithelial marker cytokeratin 20 CK20 stains positive with immunohistochemistry in a vast majority of MCCs. MCC continues to have a high mortality characterised by high recurrence and early metastases.
Merkel cell carcinoma is a neuroendocrine skin carcinoma caused by the Merkel cell virus and ultraviolet radiation. Merkel cell carcinoma MCC is a rare rapidly growing and highly malignant cutaneous tumor that typically presents in elderly males as an erythematous or violaceous plaque or nodule in sun-exposed areas. Immunosuppression-associated accounts for nearly 8 of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma.
The diagnosis of MCC is possible only immunohistochemically by using the wide spectrum of antibodies characteristic of microscopically similar tumors. The authors investigated cytokeratins CKs 56 7 17 and 20 staining in paraffin sections of 26 Merkel cell carcinomas to expand the knowledge of the CK staining profile of this entity. The tumor classically The tumor classically demonstrates positive immunohistochemistry IHC staining for chromogranin AChrA cytokeratin 20 CK20 neuron specific enolase.
The clinical and morphological picture of Merkel cell carcinoma MCC may be rather challenging. Therefore the immunohistochemical profile plays a relevant role in confirming the microscopic diagnosis. Merkel cell carcinoma MCC of the skin is a rare aggressive malignant neuroendocrine neoplasm.
Merkel cell carcinoma is a highly aggressive type of skin cancer that was first described by Cyril Toker in 1972 as trabecular tumor of the skin.

Immunohistochemistry Of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus T Antigen With Cm2b4 Download Scientific Diagram

Early B Cell Differentiation In Merkel Cell Carcinomas Clues To Cellular Ancestry Cancer Research
Komentar
Posting Komentar